Telehealth Trends 2026: Key Insights Into the Future of Virtual Care
Table of contents
- What Is The Future of Telehealth?
- Telehealth at Present
- Telehealth Industry Trends Worldwide
- Focus on mental health
- Hybrid care model
- Chronic care management
- AI and wearables integration
- Global expansion and policy adaptation
- Telehealth Industry Trends in 2026
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI assistants and chatbots
- Diagnostics and imaging
- Predictive analytics and cognitive computing
- Intelligent patient monitoring
- AI-powered decision trees and care coordination
- Digital twin health modeling
- Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- Big Data & analytics
- Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR)
- Personalized digital therapeutics (DTx)
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM)
- Telepharmacy
- Barriers to Telehealth Development
- Tendency for in-person visits
- Unequal telehealth distribution
- Mistrust of technology
- Regulatory barriers
- Bottom Line
What Is The Future of Telehealth?
Telehealth, an innovative healthcare delivery service that connects patients to medical workers via videoconferences or other wireless communications, isn’t something new. The earliest use of the technology dates back to the early 1960s when Nebraska Psychiatric Institute and Norfolk State Hospital created a connection with a close-circuit television link, which marked the beginning of telepsychiatry. In fact, this technology has been used in Australia for several decades to provide health services to remote communities throughout the country.
COVID-19 has become a strong impetus for the development of telemedicine and determined its popularity today. Indeed, since the beginning of the pandemic, according to McKinsey the use of telehealth has increased 38 times since before the pandemic various trends and valuable use cases have emerged in this industry.
Although technology has taken a confident position and telehealth software development services are increasingly requested, some believe its popularity was determined only by temporary circumstances like COVID restrictions, and shortly, the boom will subside. At the same time, many healthcare experts continue to argue that telehealth growth is just beginning and are pushing for expanding telehealth coverage in the future.
Below, we'll figure out the leading trends in telehealth for 2026. Stay tuned!
Telehealth at Present
The telehealth industry is thriving, with notable advancements and widespread adoption reshaping modern healthcare delivery. Thus, in 2026, the global telemedicine market is estimated to surpass $175 billion and is on a clear trajectory to reach over $709.69 billion by 2034. This growth reflects increased investment in digital healthcare technologies, a response to ongoing healthcare demands, and a shift toward patient-centered care models.
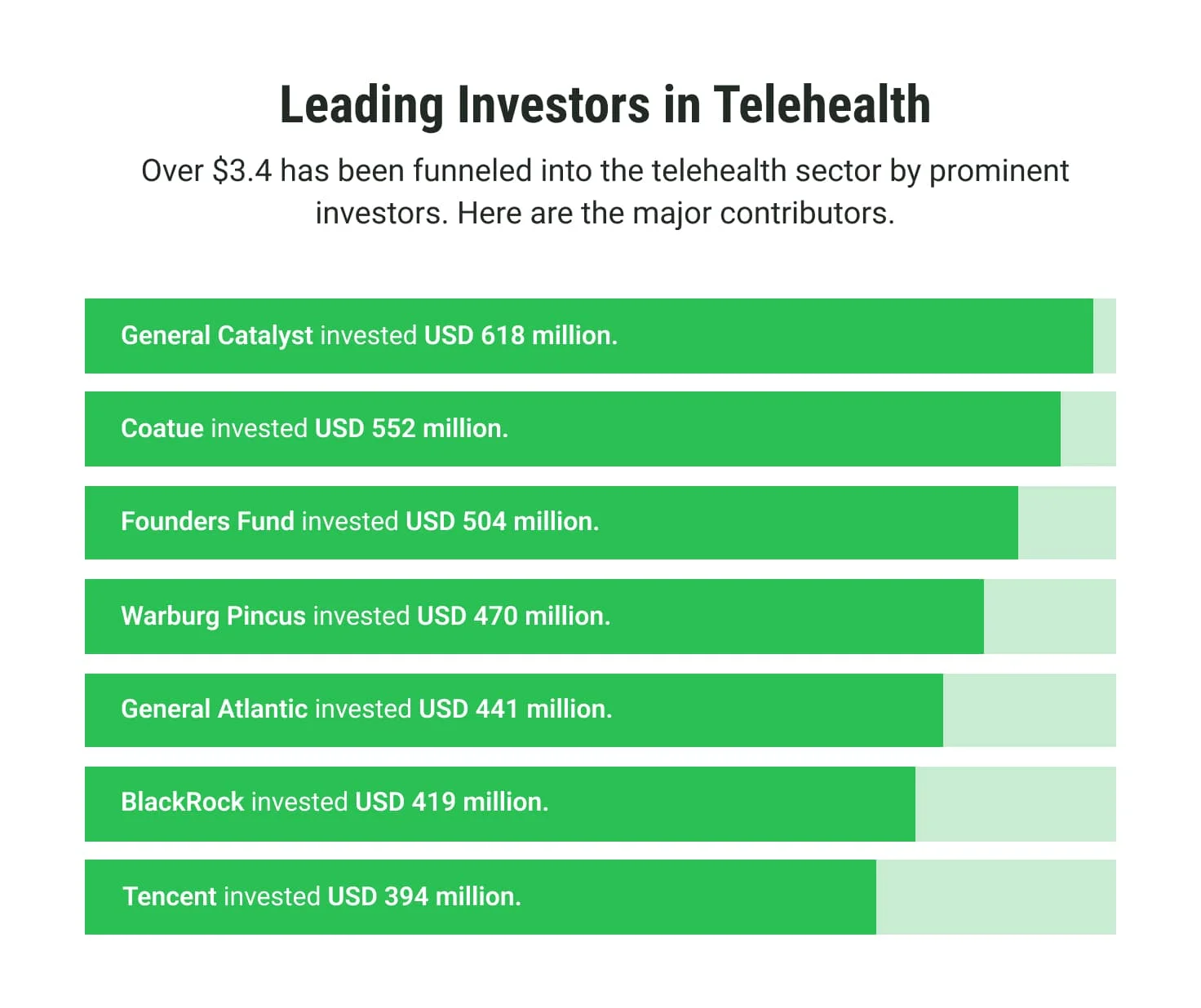
Enhanced accessibility and cost-effectiveness make telehealth a cornerstone of healthcare innovation. Key players, including General Catalyst, Coatue, Founders Fund, General Atlantics, and others, are fueling the sector's innovation. These investors focus on solutions that skyrocket accessibility and leverage AI-powered platforms, smart wearables, and patient-centric technologies. In 2022 alone, funding in telehealth reached $3.4 billion, showcasing robust confidence in its transformative potential.
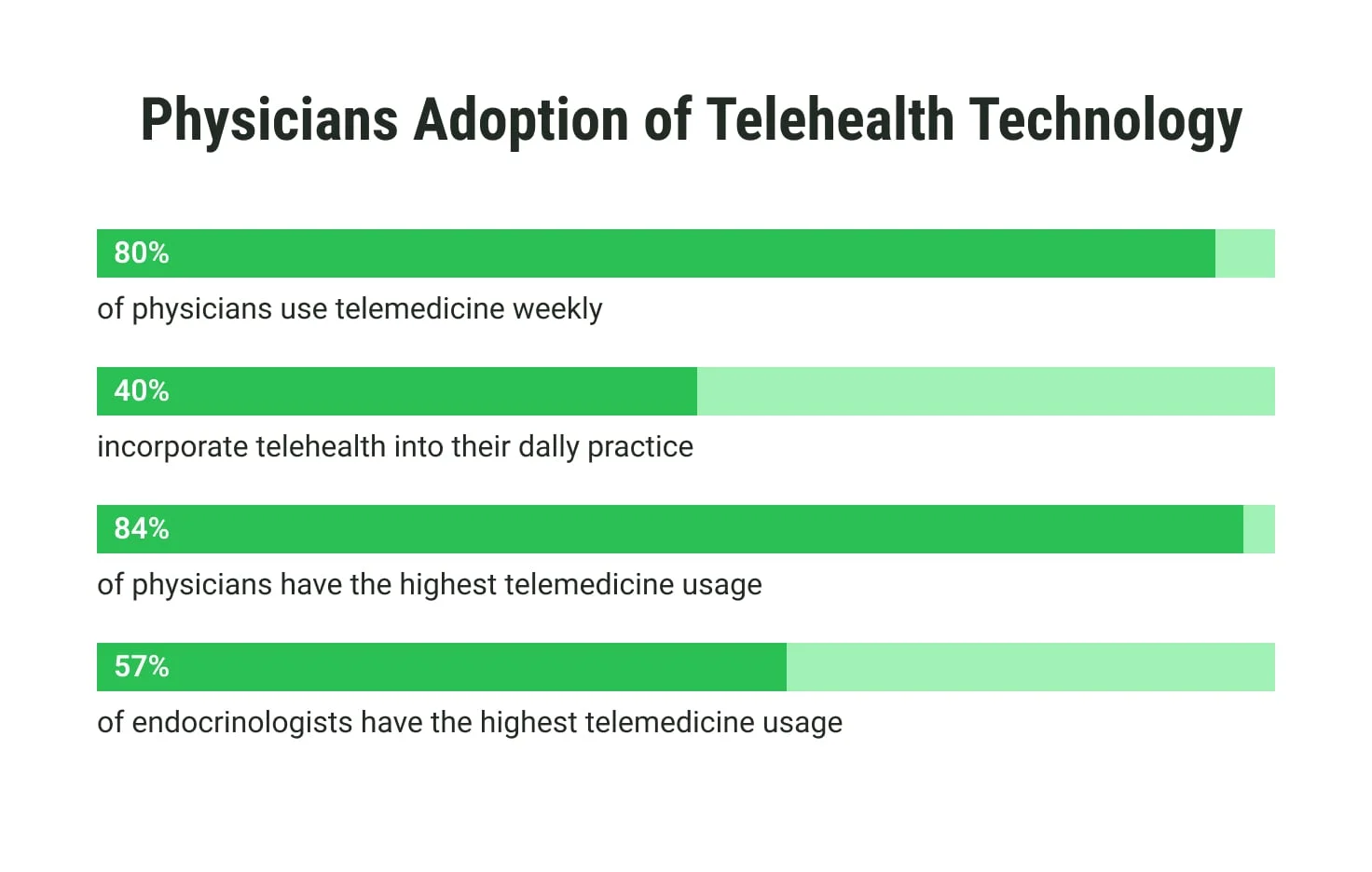
Physician adoption remains strong, with more than 80% of healthcare providers integrating telehealth post-pandemic. The convenience of virtual care, particularly for chronic condition management and follow-ups, continues to drive this trend. Innovations in software and interoperability solutions ensure telehealth is seamlessly incorporated into modern healthcare practices.
 These developments signal a promising future, positioning telehealth as a critical driver of healthcare innovation.
These developments signal a promising future, positioning telehealth as a critical driver of healthcare innovation.
Telehealth Industry Trends Worldwide
The global telehealth industry is rapidly evolving, embracing diverse innovations to meet modern healthcare needs. Below, we consider the key trends shaping the sector globally.
Focus on mental health
Telehealth is revolutionizing mental healthcare by improving accessibility and reducing stigma. Virtual therapy sessions, AI-driven mental health assessments, and 24/7 crisis support platforms are now integral and help to address the rising demand for psychological well-being services.
Hybrid care model
The hybrid model, which blends in-person consultations with virtual care, is becoming a standard. It ensures patients receive personalized and flexible care while allowing providers to optimize resources and efficiency.
Chronic care management
Telehealth solutions are pivotal in managing chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease. Remote monitoring, connected devices, and tailored care plans empower patients to maintain health from home while reducing hospital visits.
AI and wearables integration
Integrating AI and smart wearables offers real-time health tracking and predictive insights. These technologies enhance diagnostic precision and allow for proactive interventions in patient care.
Global expansion and policy adaptation
The adoption of telehealth is accelerating worldwide, with governments implementing policies to ensure equitable access and interoperability. This global push fosters innovation and bridges care gaps across underserved regions.
Telehealth Industry Trends in 2026
Breakthrough technologies and approaches that redefine patient care and healthcare delivery will shape the telehealth landscape in 2026. Below, we offer an overview of the key trends driving the industry forward.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI development and AI-based solutions are central to telehealth advancements.
AI assistants and chatbots
AI assistants and chatbots are revolutionizing telehealth by providing 24/7 patient support. These tools enhance communication, automate appointment scheduling, and answer routine questions, freeing healthcare professionals for complex tasks. AI-based solutions can be seamlessly integrated into the existing telehealth platforms, improving accessibility and efficiency.
Diagnostics and imaging
AI-powered tools transform diagnostics and imaging by analyzing vast datasets to detect diseases quickly and accurately. These solutions reduce the possibility of human error, assist radiologists, and provide earlier intervention opportunities, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Predictive analytics and cognitive computing
AI leverages predictive analytics to anticipate health risks, identify trends, and personalize care strategies. Cognitive computing enables systems to process complex data patterns, offering actionable insights for enhanced clinical decision-making.
Intelligent patient monitoring
Advanced AI algorithms continuously analyze patient data, enabling real-time monitoring and timely alerts for critical health changes. Implementing AI-based solutions ensures better management of chronic conditions and supports healthcare providers in proactive care delivery.
AI-powered decision trees and care coordination
AI-driven decision trees streamline clinical workflows by providing tailored care recommendations. These tools optimize coordination among healthcare teams, ensuring consistent, high-quality patient care across various touchpoints.
Digital twin health modeling
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of patients, simulating potential treatment outcomes. This innovative approach empowers providers to test interventions, predict complications, and design personalized treatment plans, leading to better patient care.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
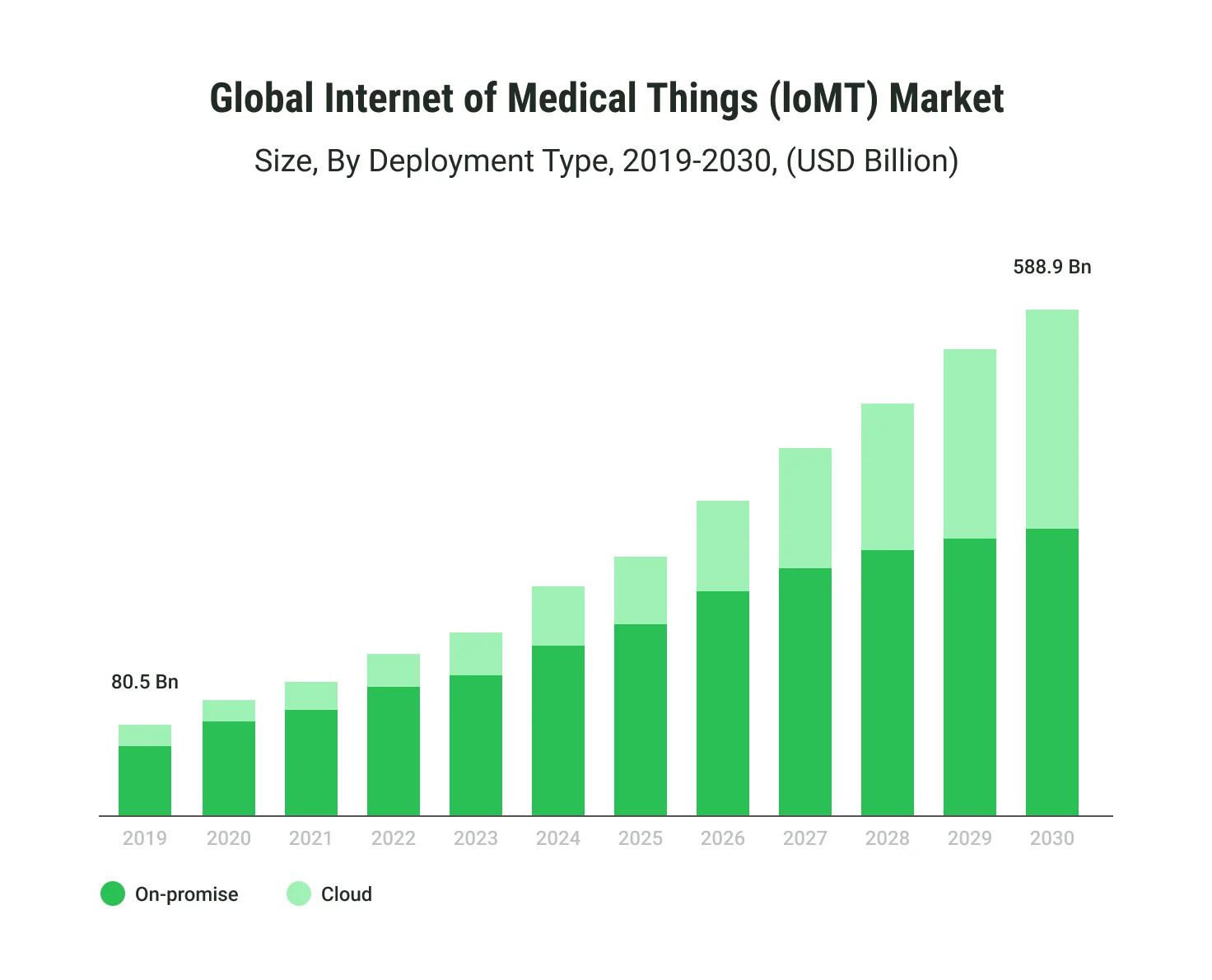
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) market is projected to skyrocket from $80.5 billion in 2019 to $588.9 billion by 2030, demonstrating robust growth fueled by an increasing demand for connected healthcare solutions. IoMT seamlessly integrates wearable devices, hospital systems, and home-based tools, enabling real-time data exchange and intelligent health monitoring.
Cloud-based IoMT solutions are also gaining momentum, offering scalability and cost-efficiency, while on-premise solutions remain valuable for secure, localized data management. This integration significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy, optimizes workflows, and improves patient outcomes, particularly in remote patient monitoring (RPM) and personalized care systems.
Big Data & analytics
Telehealth thrives on data analytics services that revolutionize telehealth decision-making processes. Advanced data-driven insights enable providers to identify trends, predict patient outcomes, and enhance care delivery.
How can Big Data be used in telehealth?
Big Data transforms telehealth, offering unparalleled insights and enabling proactive care strategies:
- Predictive analytics for early intervention
Big Data empowers healthcare providers with tools like time-series analysis to forecast potential health issues, enabling early intervention based on historical data trends.
- Personalized treatment plans
Using digital phenotyping and biosensor data, providers craft tailored treatments that account for genetic, lifestyle, and biometric factors.
- Remote patient monitoring and alerts
Wearables and anomaly detection algorithms deliver real-time health updates, enabling immediate responses to irregularities.
- Population health management
Data aggregation identifies health trends across populations, guiding preventive measures and resource allocation.
- Operational efficiency
Prescriptive analytics optimize workflows by analyzing usage patterns, recommending efficient actions, and streamlining operations.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR)
AR and VR are becoming indispensable for training, diagnostics, and even remote surgery simulations. AR technologies enhance telemedicine's effectiveness by creating immersive experiences for both patients and healthcare providers:
- Training and education
AR/VR-based simulations replicate clinical scenarios, enhancing medical training through 360-degree video and spatial computing.
- Chronic care management
Therapeutic VR solutions like AppliedVR address chronic pain through immersive, tactile experiences.
- Rehabilitation and telesurgery
AR enhances precision in telesurgery and virtual rounds, facilitating remote consultations.
- Surgical planning and assistance
Real-time 3D imaging aids surgeons by visualizing anatomy during procedures.
- Innovative implementations
Applications include 3D bioprinting, biometric gateways, and WebXR tools for real-time surgical guidance.
Personalized digital therapeutics (DTx)
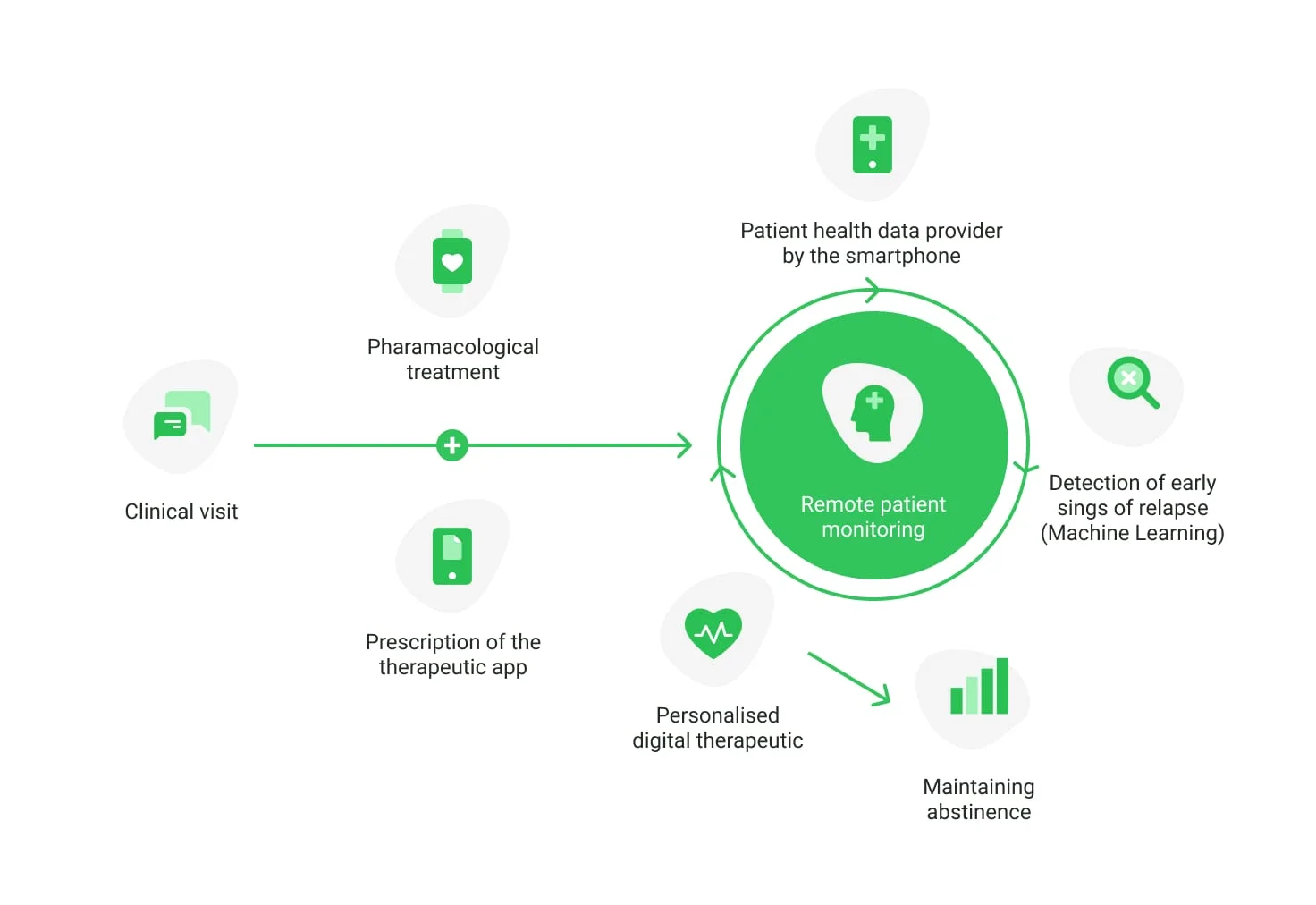
DTx offers tailored digital solutions to support disease management, preventive care, and therapy adherence. These applications integrate with telehealth platforms to provide more effective, patient-specific treatment strategies.
Key aspects of personalized DTx include:
- Remote therapeutic monitoring (RTM)
Connected devices track real-time progress, tailoring treatments as patients evolve.
- Patient-reported outcomes (PRO)
Digital diaries enable patients to log symptoms, helping providers refine therapeutic strategies.
- Virtual rehabilitation & self-guided therapy
Apps like SilverCloud and Woebot empower patients with CBT-based modules and mental health tools.
- Psychoeducation platforms
Programs deliver mental health education while monitoring behavioral changes with AI-driven solutions.
- Clinical decision support systems (CDSS)
Integration with CDSS ensures data-driven, real-time treatment adaptations, enhancing outcomes.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM)
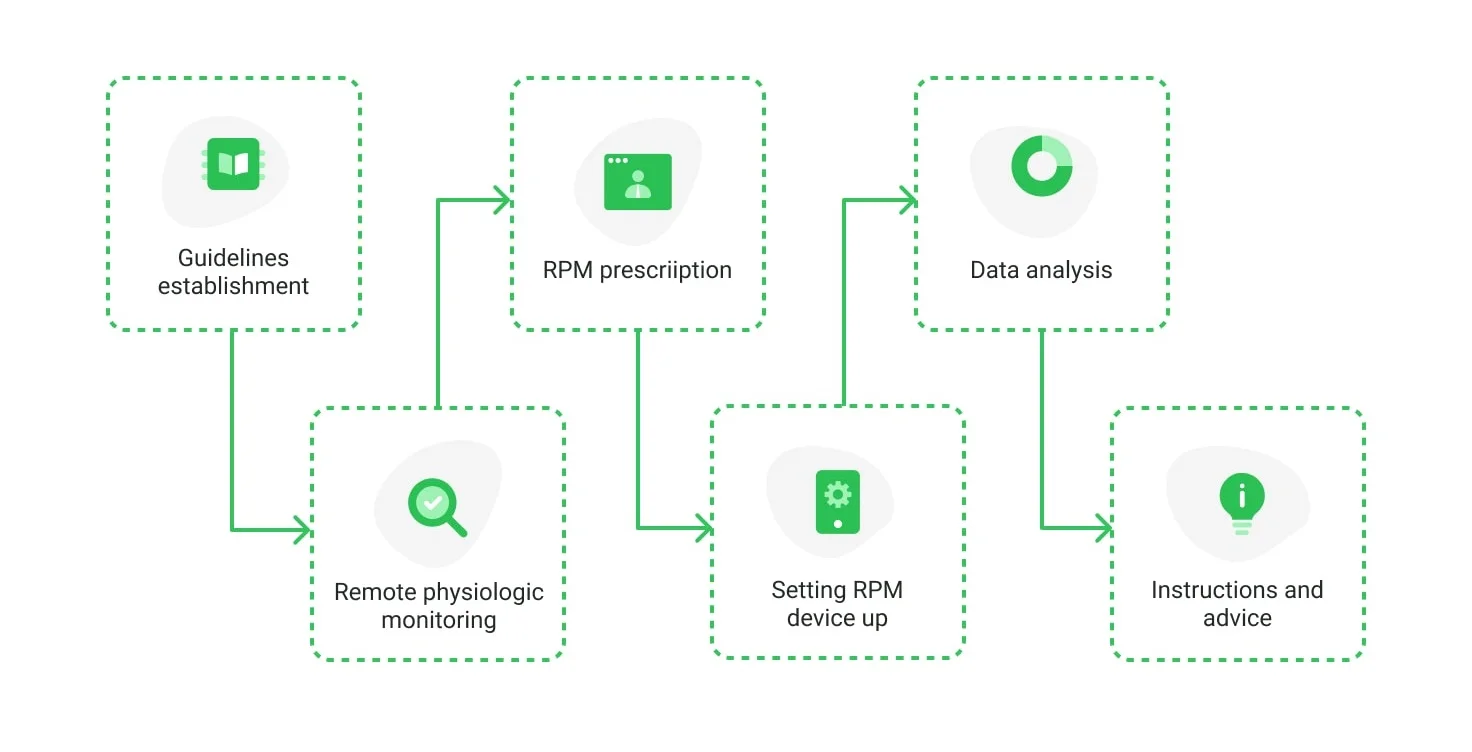
RPM continues to be a cornerstone of telehealth, allowing providers to monitor patient conditions in real time using advanced devices. This trend empowers better management of chronic diseases while reducing hospitalizations.
Essential benefits of remote patient monitoring
RPM leverages IoMT and wearables for seamless healthcare delivery:
- Real-time data collection
Devices like ECGs, pulse oximeters, and glucose monitors provide constant health monitoring.
- Immediate alerts
Automated alerts notify providers of critical changes, allowing prompt intervention.
- Patient empowerment
Custom mHealth apps foster active patient participation in health management.
- Home-based care
RPM supports quality care at home, minimizing hospital visits and improving accessibility.
Telepharmacy
The rise of telepharmacy ensures patients can access medications and consult pharmacists remotely. This trend supports medication adherence and enables timely interventions, especially for underserved populations.
According to statistics, already in 2020, over 70% of patients preferred digital healthcare access, and telepharmacy is well-positioned to meet demand. Recent regulatory shifts support innovations like remote prescription adherence tracking and chronic care management.
Telepharmacy offers the following benefits:
- Remote dispensing: automated solutions ensure fast delivery in remote areas.
- Medication therapy management (MTM): Predictive analytics reduce chronic care costs by anticipating prescription needs.
- Refill management: Automated services improve medication adherence and lower hospital readmissions.
- Advanced digital tools: Digital labeling and real-time decision-making adapt to patient-specific requirements.
Barriers to Telehealth Development
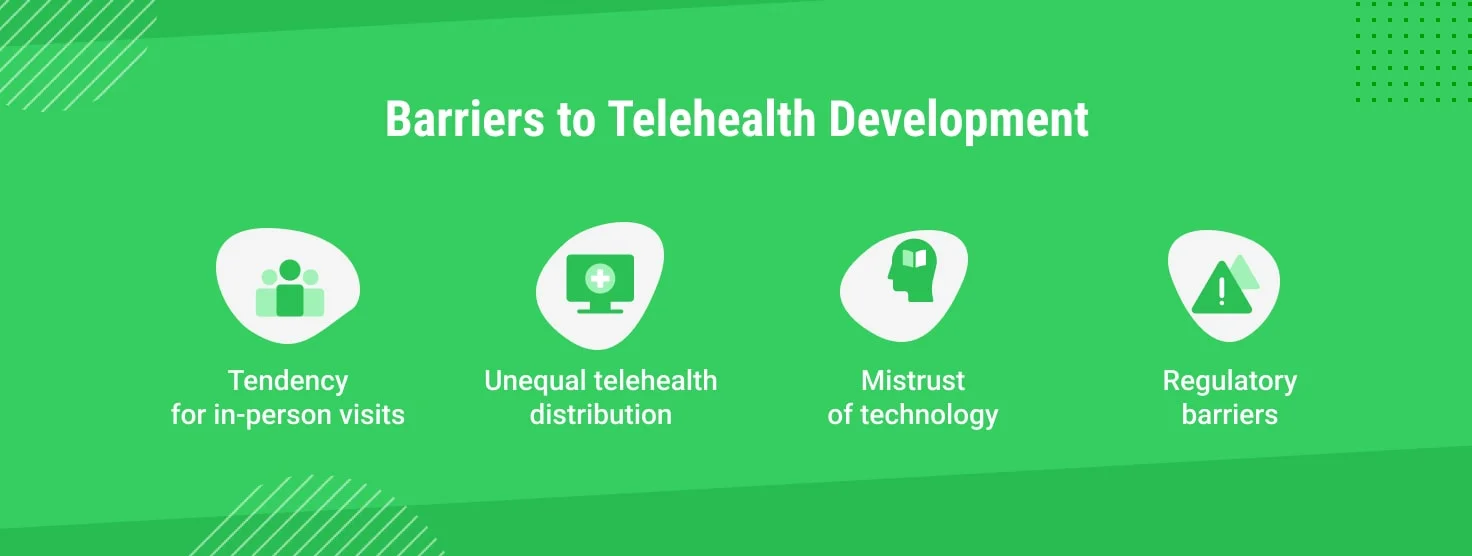
While telehealth continues to grow as a transformative healthcare tool, several barriers hinder its widespread adoption and implementation. Understanding these challenges is essential for shaping its future.
Tendency for in-person visits
Despite technological advancements, many patients prefer traditional in-person consultations. Reasons include the perception that physical examinations are more thorough, a sense of personal connection with providers, and a need for familiarity with telehealth platforms. Bridging this gap requires education on telehealth's capabilities, improved user experiences, and hybrid care models that combine remote and in-person options.
Unequal telehealth distribution
Access to telehealth services varies significantly across regions and demographics. Urban areas often benefit from robust internet infrastructure, while rural and underserved communities may face connectivity issues, limited provider availability, or technological disparities. Addressing this inequity involves investing in broadband expansion, subsidizing technology, and training healthcare workers in telehealth best practices.
Mistrust of technology
Some patients and providers still need to be convinced about telehealth's reliability, privacy, and security. Concerns about data breaches, misdiagnoses, and impersonal care contribute to this mistrust. Building confidence requires transparent communication about security measures, compliance with international data protection standards, and showcasing telehealth's proven successes.
Regulatory barriers
Telehealth regulations are complex and vary significantly between countries and even states. In the U.S., for instance, issues like licensing restrictions, reimbursement policies, and cross-state practice rules complicate implementation. Globally, inconsistent frameworks and data-sharing laws add further challenges. Policymakers must harmonize regulations, expand provider licensing, and ensure equitable reimbursement practices to create a more supportive environment for telehealth.
By addressing these barriers with strategic investments and policy reforms, the telehealth industry can unlock its full potential and deliver accessible and equitable care worldwide.
Bottom Line
The telehealth industry is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the pressing need for accessible healthcare. From integrating AI-powered tools and IoMT solutions to developing personalized digital therapeutics, telehealth trends are transforming healthcare delivery.
Despite barriers like regulatory challenges or mistrust of technology, the industry's potential remains immense. By addressing these hurdles and embracing innovation, telehealth can continue to revolutionize global healthcare, making quality care more accessible, efficient, and patient-focused than ever before.
Updated on Jan 1, 2026





