Bridging e-Learning and Telehealth: Real Value for Medical Education and Training
Table of contents
With the outbreak of Covid-19 in 2020, every sector of society was forced to reimagine, reorder, and restructure, and healthcare wasn’t an exception. Medical institutes around the globe were widely affected by Covid-19. Concerns regarding the transmission of the infection have required medical schools to provide robust, easily accessible virtual education options, which contributed immensely to developing new innovative solutions.
Telehealth was the medical field’s response to this pandemic. It is worth mentioning that telehealth is not a new phenomenon. For decades, there have been government-funded services to provide healthcare telephonically to remote sites both on the earth and in the air. However, the Covid-19 pandemic and the subsequent global lockdown laid a solid foundation for telehealth’s subsequent successful development.
Let’s take a closer look at this technology to rigorously evaluate its effects on medical learners and predict its future.
Telehealth Today
Telehealth today is one of the most promising directions in healthcare and e-learning. Telemedicine statistics show that the use of virtual care is 38 times higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic, and both providers and patients are happy with their experiences.
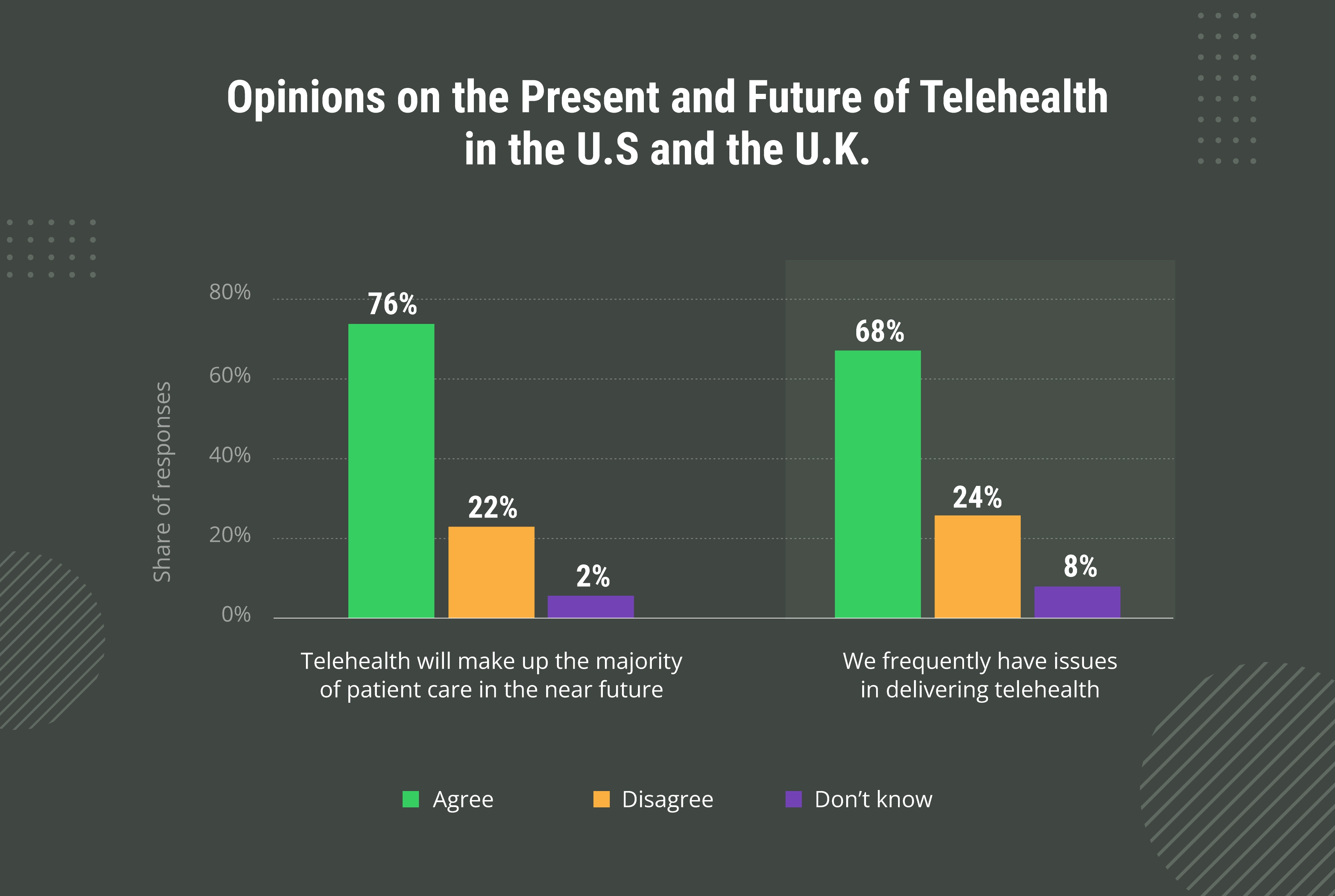
According to another survey carried out among clinicians in the United States and the United Kingdom in 2021, 76 percent of respondents agreed that telehealth would make up most patient care in the near future. However, 68 percent reported they frequently had issues in delivering telehealth to patients.
Custom telehealth solutions are widely used to satisfy the needs of both healthcare professionals and patients. Some of the most widespread use cases of telemedicine today are created for administrative management and the provision of remote patient care, which includes teleconsultations, telemonitoring, and telesurgery.
Another phenomenon that is growing in popularity nowadays is telemental health. The technology provides new opportunities for patients who can now access care from the privacy and safety of their homes, as well as unlocks excellent potential for mental health providers.
Due to its great capacity, telehealth today will show real value for all parties involved. However, let's focus on what opportunities this technology opens up for healthcare specialists and students in terms of medical education and training.
Telehealth Innovations in Health Education: Two Use Cases That Are Still Relevant in the Post-Pandemic Period
The mobile app market offers a wide range of new solutions for healthcare professionals. These solutions differ in their purpose and target audience, from professional certification and recertification apps to continuing medical education systems. Still, they are becoming particularly valuable for graduate and postgraduate education in the health professions.
Leveraging the vast potential of telehealth in telelearning, telementoring, telesurgical planning environments, telerobotic surgery, and teleconsultation enables forward-thinking institutions to teach anything, anytime, anywhere. Moreover, the quality of curriculum and mentorship is the same as in standard classroom settings, emphasizing skill mastery rather than information mastery. The following are some examples of trendy directions that are gaining popularity in the tech world.
Telehealth for promoting rural workforce education and training
According to statistics, over one quarter (28.0%) of the EU-28 population lived in a rural area in 2015. Research shows that the healthcare needs of individuals living in rural areas are different from those in urban areas, and rural areas often suffer from a lack of access to healthcare. Such challenges as economic and educational disparities, coupled with rural isolation, present hurdles in the recruitment and retention of a skilled workforce in these areas.
Though the rural population has been decreasing, telehealth technology is still beneficial for them. Telehealth can be used to help the rural health workforce overcome barriers to receiving education and training and allow providers to meet the evolving needs of their patients. Instead of traveling for continuing education, rural providers can access telehealth technology, such as Microsoft-developed HoloLens and other AR/VR-based solutions, to receive face-to-face instruction and demonstrate the skills they have acquired through distance learning.
To ensure the demand for telehealth is growing in rural areas, let’s look at the statistics regarding the use of telehealth in east-central Canada.
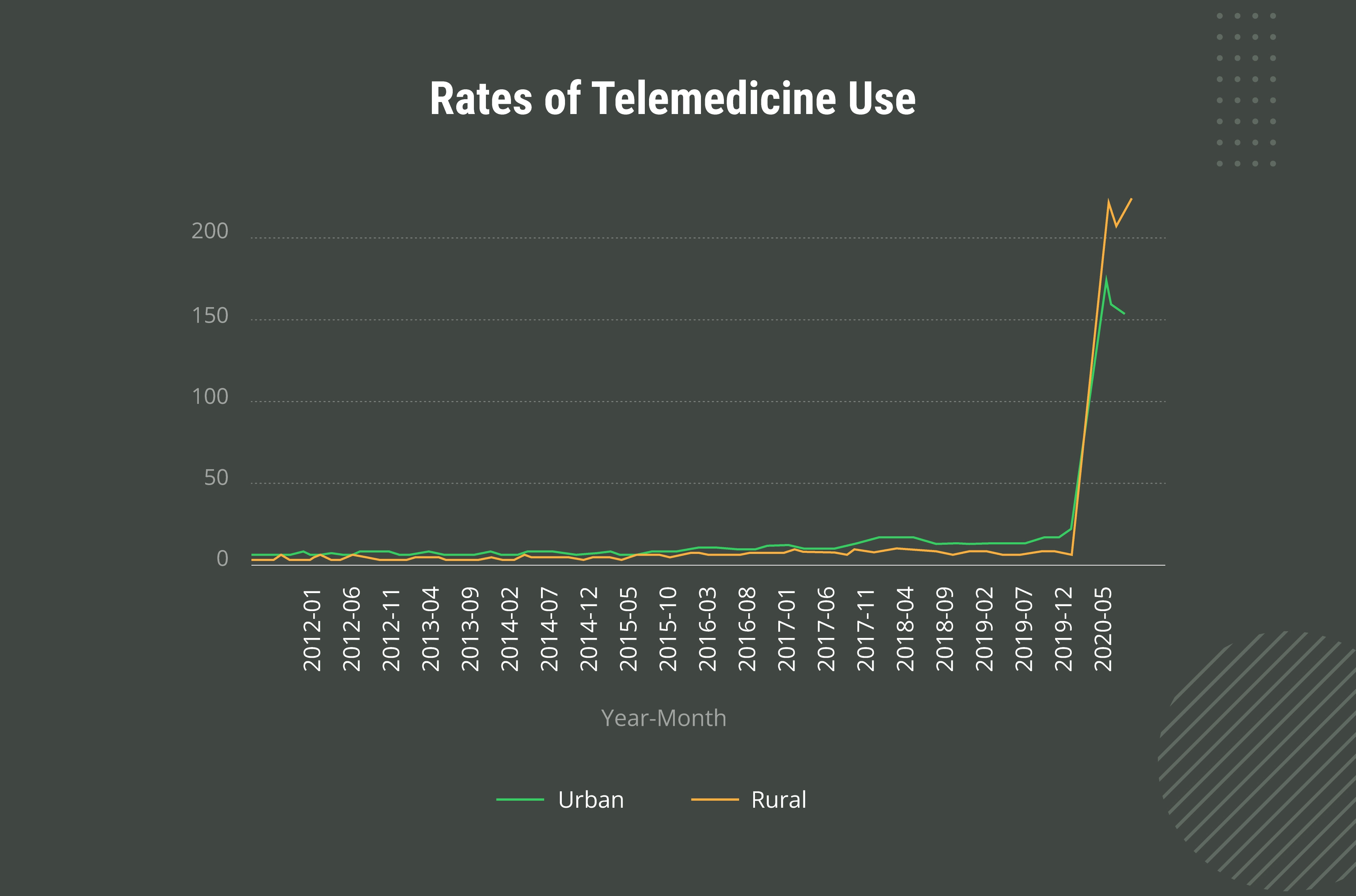
Many distance education courses use telehealth technology to deliver aspects of their curriculum. Providers in rural areas can also receive telementoring from specialists located elsewhere in order to build their capacity to address complex cases.
Medical students from Creighton University in Omaha, Nebraska, and the University of Alaska-Anchorage have already leveraged a unique hybrid distance education program to learn occupational therapy and earn their doctorate degrees regardless of the location. The program includes online courses and video conference tools, and clinical adjunct faculty in Alaska serve as mentors in the field and assist the Nebraska faculty by teaching the lab and experiential components of the program.
Telehealth for connecting geographically separated specialists
Sharing new experiences and doing collaborative research are essential for doctors who want to grow professionally in their field. Doctors may use telehealth websites to build support networks to exchange their skills and provide better healthcare services.
Telemedicine can also be used in a special environment where surgical students, geographically separated, can collaboratively learn and interact with specialists and even plan surgeries. Being combined with Augmented Reality, such a solution can be more immersive, allowing doctors and their teams to watch a 3D monitor when performing surgical procedures. By using video conferencing, physicians and even surgeons will work on people that are thousands of miles away. This enables even intercontinental medical teams to collaborate and hold video meetings on complex and urgent situations.
Of course, surgical skills training cannot be replaced easily by videos, as a high level of tutor-student interaction is required. Thus, the University of Hong Kong developed a new web-based surgical skill learning session (WSSL) for better interaction between surgeons. Let’s look at what such sessions look like:
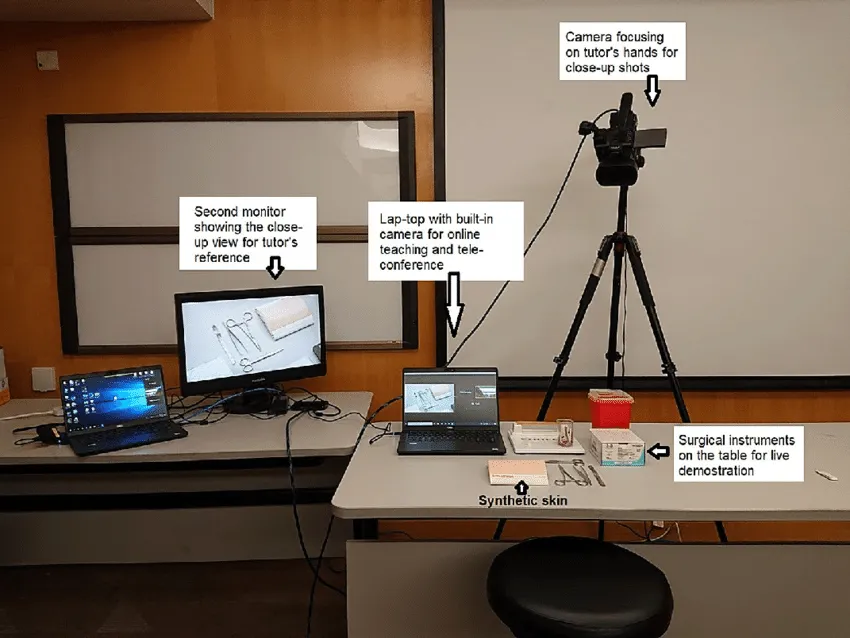

The system allows analyzing a surgeon's hand and surgical tool movements and detects features like smoothness, efficiency, and preciseness. The solution is capable of providing both real-time feedback and a performance score at the end of the surgery.
In a Nutshell
Key health tech trends have emerged surrounding the use of telehealth and e-learning and they will continue to shape the future of these technologies. While some believe that no innovation can replace real practice and real communication with specialists, others consider telemedicine as a major aspect of the revolution in the health industry. Anyway, in light of the aforesaid benefits, it is envisaged that telehealth will gain further momentum and become an indispensable part of the interaction between healthcare professionals and patients.
Our experts have rich experience in delivering solutions to the healthcare sector, and telehealth is no exception. Want to develop your own telehealth from the scratch app or add the e-learning features to the already existing solution? Our team is ready to provide a wide range of services aimed at helping your business to get the most out of telemedicine technology. Book a free consultation!
Updated on Apr 21, 2025





